Contents
Introduction to Female Hair Loss
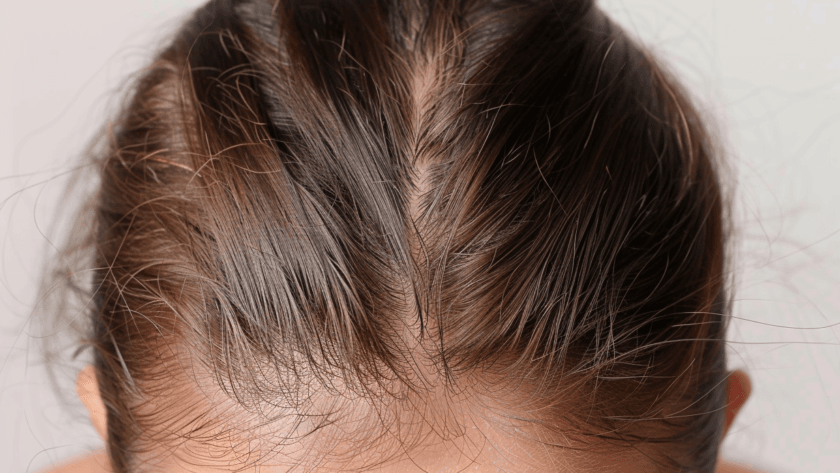
Many women experience hair loss due to various reasons, such as genes, hormonal changes, health issues, and lifestyle habits. One common type, called androgenetic alopecia or female-pattern hair loss, usually starts with thinning hair at the crown and scalp. Women can also face other types of hair loss, like alopecia areata, telogen effluvium, and traction alopecia, each affecting hair thinning or loss in different ways.
Common Types of Female Hair Loss
Androgenetic Alopecia: Female-Pattern Hair Loss
Androgenetic alopecia, or female-pattern baldness, is the most prevalent type of hair loss in women. This hereditary condition often begins with thinning hair on the crown or a widening of the part. Unlike male-pattern baldness, it rarely leads to complete baldness but can significantly impact self-esteem. The condition typically worsens with age and is especially noticeable after menopause due to hormonal changes.
Telogen Effluvium: Stress-Induced Hair Shedding
Telogen effluvium occurs when a large number of hair follicles enter the resting phase of the hair growth cycle, leading to noticeable shedding. This condition is often triggered by significant stress, hormonal changes, or nutritional deficiencies. Events such as childbirth, major surgery, or drastic weight fluctuations can also cause telogen effluvium. While this type of hair loss is usually temporary, addressing the root cause is essential for regrowth. If you’re dealing with a lot of stress due to social anxiety try this toolkit!
Alopecia Areata: Patchy Hair Loss
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder that causes sudden, patchy hair loss on the scalp or other parts of the body. The condition can occur at any age but is most common in younger individuals. While some women experience regrowth in the affected areas, others may face recurrent episodes, making the condition unpredictable.
Traction Alopecia: Hair Loss from Styling Practices
Traction alopecia results from prolonged tension on the hair caused by tight hairstyles such as ponytails, braids, or extensions. Over time, this tension damages hair follicles, leading to hair thinning or bald patches. If detected early and the styling habits are changed, this type of hair loss can often be reversed.
Causes of Hair Loss in Women
Genetic Predisposition
One of the most common causes of hair loss in women is genetics. Conditions like androgenetic alopecia often run in families, with symptoms becoming more apparent as women age.
Hormonal Changes and Imbalances
Hormonal fluctuations due to life events such as pregnancy, childbirth, or menopause can significantly impact hair growth cycles. For example, postpartum hair loss is a temporary condition caused by a drop in estrogen levels after pregnancy. Similarly, the hormonal changes during menopause can result in thinning hair and increased shedding.
Medical Conditions Affecting Hair Growth
Certain medical conditions contribute to female hair loss. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, and autoimmune diseases like alopecia areata disrupt normal hair growth and lead to noticeable thinning or shedding.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Lifestyle choices and environmental influences also play a role in female hair loss. Chronic stress, poor diet, and certain hairstyling practices can weaken hair and exacerbate hair loss. Nutritional deficiencies, particularly in iron, zinc, and biotin, are common culprits. Identifying and addressing these factors can help improve hair health.
Treatments and Solutions for Female Hair Loss
Medical Treatments for Hair Regrowth
Topical and oral medications are often the first line of defense against female hair loss. Minoxidil, an over-the-counter topical treatment, is widely recommended for stimulating hair growth. Prescription medications such as finasteride are effective for postmenopausal women experiencing severe thinning.
Lifestyle Adjustments to Support Hair Health
Adopting a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, including biotin, iron, and zinc, can strengthen hair follicles and promote growth. Incorporating stress-management techniques, such as mindfulness, yoga, or meditation, can also help mitigate stress-induced hair loss.
Nutritional Supplements for Hair Growth
Specialized supplements, such as collagen peptides and multivitamins designed for hair health, can provide the body with additional nutrients needed for optimal hair growth.
Cosmetic and Surgical Options
For women seeking immediate aesthetic solutions, wigs, hair extensions, or hair toppers can be effective options. Hair transplant surgery is another choice for those looking for a more permanent solution, though it requires careful consideration due to the cost and recovery time involved.
Conclusion
Female hair loss is a complex issue influenced by genetics, hormones, medical conditions, and lifestyle choices. While the physical symptoms can be distressing, the emotional impact is equally significant. By understanding the various types of hair loss, their causes, and available treatments, women can take proactive steps to manage their condition effectively. Seeking professional guidance is an essential first step toward reclaiming not only hair health but also confidence and self-esteem.